Laboratory pipettes are essential instruments in any scientific environment, designed for the accurate transfer of liquids in small volumes. These tools are crucial for performing experiments that require accuracy in the measurement and handling of liquid substances.
What do laboratory pipettes look like?
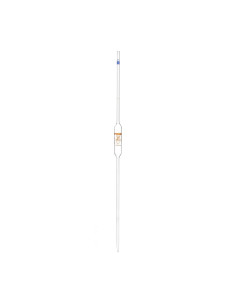
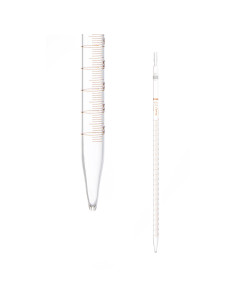
Pipettes vary in shape and size, but are generally cylindrical and made of glass. Some pipettes are calibrated to measure different volumes, while others are adjustable.
What are laboratory pipettes for?
Laboratory pipettes are crucial in numerous fields because of their precision in measuring and transferring liquids. In scientific research, they are indispensable for the exact dosing of reagents in methodologically rigorous experiments. In the medical field, they facilitate the preparation of solutions for diagnostic tests, ensuring reliable results. In the pharmaceutical and food industries, pipettes contribute to the precise formulation of products, ensuring consistency and quality. In the educational sector, they are essential tools for teaching laboratory techniques to students, providing a practical grounding in experimental procedures.
How are pipettes classified?
Pipettes are classified into several categories, such as:
- Volumetric or bulb pipettes: these pipettes are designed to measure a single specific volume with high accuracy. They are ideal for applications where accuracy in measuring a fixed volume of liquid is required, such as in standard solution preparations in analytical chemistry.
- Graduated or Mohr pipettes: unlike volumetric pipettes, graduated pipettes have a scale along the length of the tube that allows different volumes to be measured as needed. They are versatile and useful in situations where measurements of several volumes are required during an experiment.
- Class A pipettes: class A pipettes are laboratory instruments designed to provide the highest precision and accuracy in the measurement of liquid volumes. They are calibrated to meet strict standards, such as those defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ensuring reliable results in critical applications. They are ideal for tasks requiring high precision, such as chemical analysis and scientific research experiments.
- Class B pipettes: class B pipettes have wider tolerances than Class A pipettes, making them less accurate and suitable for applications where extreme precision is not critical.
How are laboratory pipettes used?
Using a pipette in the laboratory is a process that requires technique and precision. Depending on the type of pipette, the method may vary slightly, but generally involves the following steps:
- Aspiration: the pipette tip is placed in the liquid and a mechanism (such as a bulb or piston) is used to aspirate the liquid upwards to a specific graduated mark, ensuring that the desired volume is measured.
- Transfer: carefully transfer the pipette to the new container and dispense the liquid. The dispensing technique must be controlled to avoid bubbles or spillage, which could affect the accuracy of the measurement.
- Cleaning: after use, it is essential to clean the pipette properly to avoid cross-contamination between samples or deterioration of the instrument.
This process varies slightly depending on the pipette and also on the level of precision required by the experiment.
Is any certification required to use this type of material?
In many environments, especially in clinical and pharmaceutical laboratories, pipette users need specific training or certifications to ensure that they handle the instruments correctly and maintain the integrity of the results.
Frequently asked questions
What does the pipette do?
A pipette is a vital instrument in laboratories, designed to measure and transfer precise volumes of liquids with high accuracy. Its use is critical in a variety of scientific and technical procedures, from chemical analysis to biological experiments, where precision in liquid measurement is crucial to the validity of experimental results. Pipettes ensure that these measurements are repeatable and reliable, thus facilitating the standardisation of protocols in research and development.
How many pipettes are there?
There are numerous types of pipettes, adapted to different needs and volumes.
What is the most commonly used pipette?
Volumetric pipettes are widely used due to their accuracy and ease of use. They are commonly used in applications where accuracy in the preparation of solutions is crucial, such as in chemical experiments, pharmaceutical analysis and scientific research procedures. These pipettes are appreciated for their ability to provide accurate and consistent measurements, ensuring reproducibility and reliability of experimental results.